Nuclear Fusion Breakthrough Reach 100 Million Degree Celsius
- Istimewa
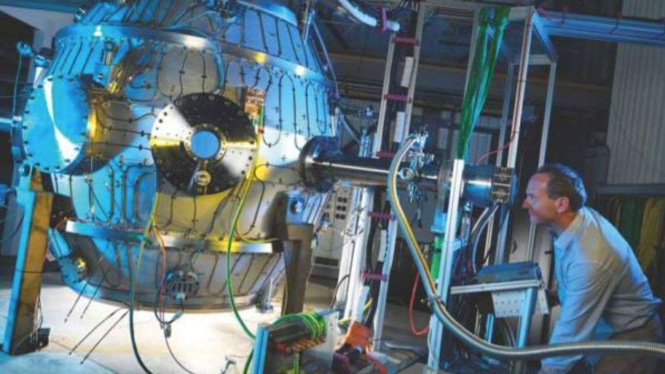
VIVA – A British company has made history after successfully realizing a nuclear fusion reaction using a spherical Tokamak machine called ST40. The resulting fusion reaction reached temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius, hotter than the Sun.
Scientists around the world are obsessed with realizing nuclear fusion reactions, like those that occur on the Sun, to produce clean energy.
They build sophisticated machines or equipment that can realize nuclear fusion reactions at temperatures around 100 million degrees Celsius.
This temperature is the threshold at which hydrogen atoms can begin to fuse into helium, which is then converted into energy.
For this reason, the Tokamak machine developed is often referred to as an artificial Sun, as it is capable of producing fusion reactions and has a temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius just like the real Sun.
Matahari
- 1486235
British scientists based in Oxfordshire in collaboration with researchers at Princeton's Plasma Physics Laboratory were able to realize the fusion reaction with the Tokamak ST40 machine.
"Ion temperatures over 100 million degrees Celsius have been generated in the compact ST40 high-field spherical Tokamak," the research team said in a new paper published in the journal Nuclear Fusion.
This was achieved using the ST40 spherical Tokamak, an apple core-shaped nuclear device in Oxfordshire.
This reactor is smaller and operates with less plasma heating power, but could pave the way for the first fusion power plant.
"Such temperatures have never been achieved in a spherical Tokamak. These temperatures can only be obtained in much larger devices with much greater plasma heating power," the researchers said.
The Tokamak ST40, first unveiled in April 2017, is spherical and more compact than the flatter and larger doughnut-shaped reactor. It was built by the Tokamak Energy company, based in Milton, Oxfordshire, to recreate the nuclear fusion process on the Sun.
Although the Sun's core burns at around 15 million degrees Celsius, the temperature of the Tokamak reactor must be much higher because the Sun has a much higher particle density.
The British-made Tokamak ST40 engine could be an alternative as it costs around US$66 million or IDR 983.5 billion.
This figure is lower than the French Tokamak machine called the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) which is estimated to cost US$22.5 billion or more than IDR 335 trillion.
As information, a fusion reaction is the merging of atomic nuclei to produce large amounts of energy. In contrast, fission reactions, which are used in atomic weapons and nuclear power plants, break down atomic nuclei into fragments (even smaller parts).
Unlike fission reactions, fusion reactions have less risk of accidents. This includes the risk of atomic material theft, but the cost of realizing both reactions (fission and fusion) is very difficult and expensive.